Email: ISP interactions best practices
Infrastructure
Altcraft Marketing Platform has flexible message transfer tuning. You can add new senders any moment. This can be necessary for several purposes:
- inbox delivery optimization
- limitations and blocks override
- faster delivery for several types of messages
- sending cost decrease
To deploy multi-sender infrastructure it is highly recommended to use a separate from domain (here and below - sender domain). This way you can use multiple from domains if needed. In any case for every sending IP address a subdomain is required for identification, PTR registration and SPF records processing.

This chapter contains only recommendations, you can use your own settings. Though this information is highly advised for better senders and ISP interaction understanding.
Make an A record for every sending domain IP address.
| Domain | Type | Record |
|---|---|---|
| mx2.s1.example.com | A | 1.1.1.1 |
| mx2.s1.example.com | A | 1.1.1.2 |
Reverse DNS lookup settings (PTR)
Reverse domain zone record is required for every sender. It should be valid and bound to a correct sender domain for every IP address you use for sending.
The reverse DNS records are maintained by your IP address provider.In case you have no direct access to these settings - make a request to your provider's technical support to make the necessary changes.
For example you have a server (s1), that has several IP addresses (1.1.1.1 and 1.1.1.2), then your domain (example.com) will have 2 PTR records:
| Domain | Type | record |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1.1.1.in-addr.arpa. | PTR | mx1.s1.example.com |
| 2.1.1.1.in-addr.arpa. | PTR | mx2.s1.example.com |
Note that IP address is reversed in domain name - this makes possible subdomain delegation to domain owners.
Incoming mail server settings for FBL/CFL
FBL/CFL (Feedback Loop or complaint feedback loop) – is a standard for notifying email senders about recipient spam complaints. It is strongly recommended to use this standard for all ISPs where possible this way or another. Usually email service providers generate a report in ARF (Abuse Report Format) containing source email and recipient email address as well as other service data, allowing email senders take necessary measures like handling spam or blocking subscription.
FBL is supported by most email-providers like Hotmail, Yahoo and AOL. To use FBL you will have to set and verify your email address from the same domain (to collect the reports) and verify your sending IP addresses. For Outlook you you will need a special agreement with Microsoft.
Gmail by Google does not generate FBL,though it uses List-Unsubscribe header to block subscriptions for users. This header can be used to provide information comparable to FBL, to identify which letters were reported as spam.

To comply with FBL standard set up an incoming mail server on your sending domain.
You can use your existing corporate server processing emails via POP3 and SMTP.
Seder domain can be different from from domain — it is explicitly specified in sender settings.
We recommend you to set up at least 3 mailboxes:
| Mailbox | Purpose |
|---|---|
| abusemaster@<domain> | Automatic ARF reports |
| postmaster@<domain> | Confirmation emails for FBL registration |
| abuse@<domain> | Mailbox recommended by abuse.net |
AKMTA contains a built-in email server. Specify in domain NS record mail processing host (MX) set within AKMTA. Thus it will receive all domain's incoming mail for all mailboxes. Messages not containing ARF reports will be redirected as configured.
If such configuration is unavailable (primary domain or corporate policies), it is still necessary to set up a subdomain for processing AKMTA mail and redirect messages from abusemaster@ mailbox on your primary domain.
Both variants are represented on the schemes below:

Email service provider FBL links
Before you make any requests make sure that:
- You have a name, phone and email of the person in charge
- You have a list of sender domains and IP addresses
- abusemaster@ mailbox is set up and able to receive mail
- postmaster@mailbox is set up and able to receive mail
| AOL | https://postmaster.info.aol.com/fbl-request |
| Comcast | http://feedback.comcast.net/ |
| Cox | http://fbl.cox.net/ |
| Earthlink | fblrequest@abuse.earthlink.net |
| Excite (Bluetie) | http://feedback.bluetie.com/ |
| Fastmail | http://fbl.fastmail.fm/ |
| Hotmail | https://postmaster.live.com/snds/ |
| Outblaze | postmaster@outblaze.com |
| Rackspace | http://fbl.apps.rackspace.com/ |
| Road Runner | http://feedback.postmaster.rr.com/ |
| Spamcop | http://www.spamcop.net/reported.shtml |
| Synacor | http://fbl.synacor.com/ |
| Terra (Brazil) | http://fbl.mail.terra.com.br/ |
| Tucows | http://fbl.hostedemail.com/ |
| USA.net | http://fbl.usa.net/ |
| Yahoo! | http://feedbackloop.yahoo.net/ |
| ZOHO | http://www.zoho.com/fbl/index.html |
| Mail.ru | https://postmaster.mail.ru/ |
| Yandex.ru | http://yandexfbl.senderscore.net/ |
| Gmail | Supports only List-Unsubscribe — a technology adding a special header to identify email complainers. Fully supported by Altcraft MP. |
Email digital signature settings (DKIM)
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) technology adds From domain digital signature to email headers. The signature is automatically verified by mail recipients which is used for reputation regulations and sending domain validation.
Messages are signed with a public key set for the sender and not known to anyone else. Public key is contained in From domain subdomain TXT record. The subdomains depend on selectors chosen. It is recommended to use unique selectors for every DKIM key. Thus you can have multiple senders with independent validation.
Keys can be created using RSA-SHA256 and RSA-SHA1 algorithms. Recommended key size is — 1024 bit.

You can check if a domain has a DKIM record with dig command:
dig TXT ak1024._domainkey.aksend.net +short
# "v=DKIM1\; k=rsa\; p=MIGfMA0G......QAB"
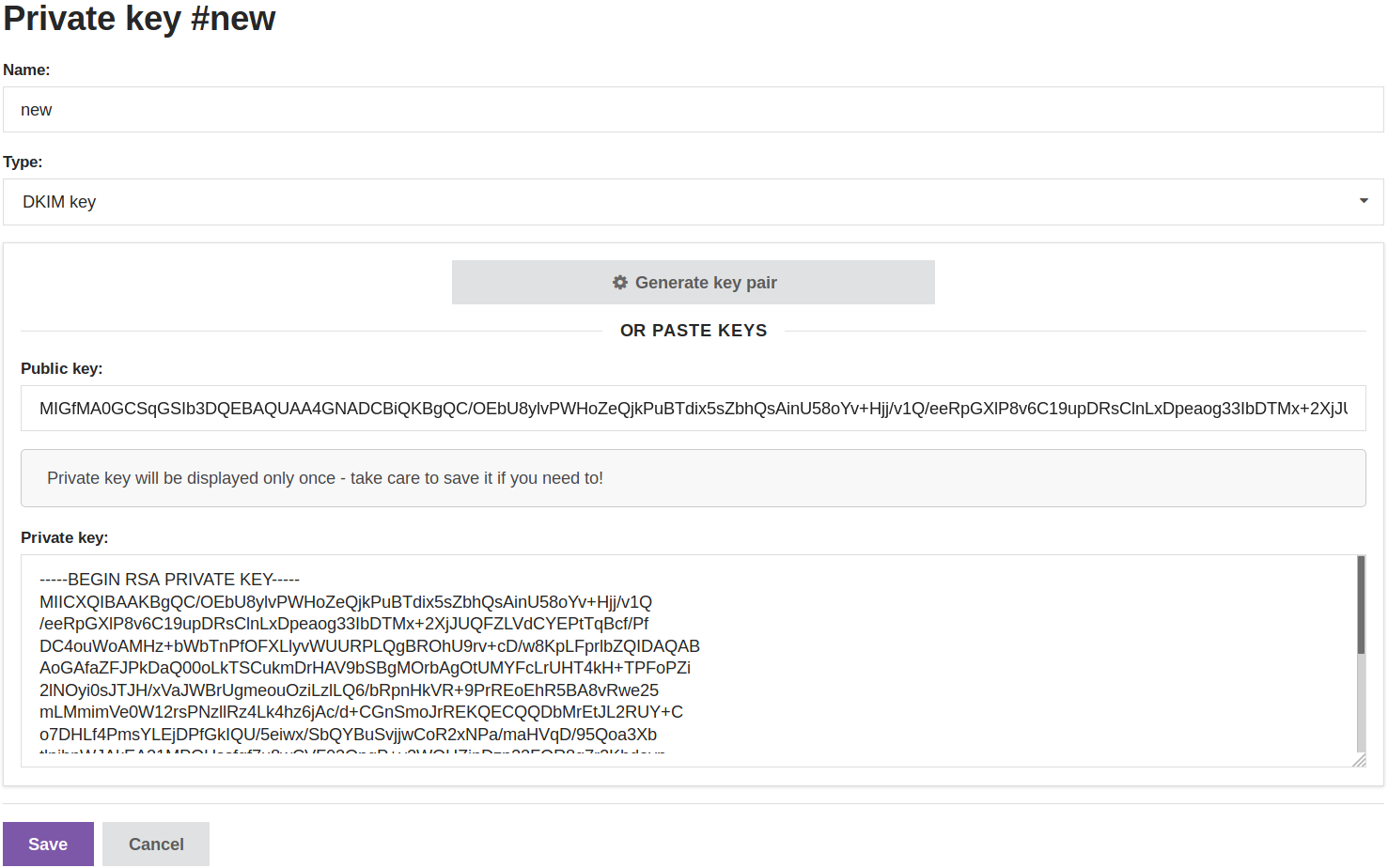
To create DKIM keys open Altcraft Marketing Platform Administrative panel and choose Setup → Keys.
Sender Policy Framework settings
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) — is a technology that allows to verify sending domain. It adds a special TXT record to specify sending from this domain for different hosts.
You can provide a list of IP addresses or use include directive to use another domain rules. This can be handy with multiple domains and changing sender IP addresses. There are also a, mx, ptr and other directives.
We recommend to add at least 3 records for different protocol versions:
| Type | Content example |
|---|---|
| SPF | spf2.0/pra include:spf.aksend.net ip4:A.B.C.D -all |
| TXT | spf2.0/pra include:spf.aksend.net ip4:A.B.C.D -all |
| TXT | v=spf1 include:spf.aksend.net ip4:A.B.C.D -all |
This example allows spf.aksend.net domain hosts and A.B.C.D. IP addresses usage. With ip4 directive you can specify separate IP addresses or a whole subnet. -all restricts sending from alternative hosts. If you want to allow any hosts for sending use +all (though it is not recommended).
You can check if a domain has a DKIM record — and view its contents with dig command as well:
Typical From domain configuration
Considering all of the above, your from domain should have a similar set of records:
| Subdomain | Type | record | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPF | spf2.0/pra include:spf.aksend.net ip4:A.B.C.D -all | SPF is considered a legacy technology so you might have problems setting it: the information here is published for backward compatibility. | |
| TXT | spf2.0/pra include:spf.aksend.net ip4:A.B.C.D -all | If the domain is currently being used for messaging add the sending IP addresses to the SPF rules. | |
| TXT | v=spf1 include:spf.aksend.net ip4:A.B.C.D -all | ||
| trk | CNAME | trk.aksend.net | |
| _dmarc | TXT | v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc@example.com; sp=none | Specify the email of the person in charge. |
| _domainkey | TXT | o=-; | |
| _policy._domainkey | TXT | o=-; | |
| ak._domainkey | TXT | v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQCldFYh3Rfrmeov+WqYYpwfW2bVUzxXPy9dSVoUCGLKCn+vgY/pdKIIBFitkvZJXGLnHqreqwGzoriEWf9ZRd+cL2LdA4UrDKheMeorBd2NSIqihkTaKz8PA+SIBFxFGm2Z0Krh5ZDF2NtFVhtD4YvqmrFqk2muzZ0tFEko8zP30wIDA |
The example below uses example.com domain. All the records are valid for ru.altcraft.com cloud messaging service.
Note that if you want to use a subdomain for messaging with Altcraft Marketing Platform, like subdomain.example.com, all records should as well be created for the subdomain (e.g. trk.subdomain CNAME ... ). At the same time root domain (example.com) SPF and policy records should allow subdomain sending.
Sender reputation
Sender reputation is the one most important parameter for successful email delivery. The right settings won't guarantee a 100% inbox delivery rate so it is critical to monitor different stages of this process.
Reputation is connected to the following entries — separately and combined:
- Sender IP
- Sender domain
- From domain
- From email
- Tracking IP
- Tracking domain
Database hygiene
Know where and how you get your subscribers — and if their contact data is valid and actual. Make sure you validate email addresses in capturing forms. If you are using double opt-in it will significantly increase chances your leads will improve your reputation. All database hygiene problems can be divide into several types:
Hard bounces. Emails cannot be delivered due to invalid email address or domain. Considerable hard bounce rates can show the data you are using is invalid. The normal value for hard bounce rate is 0,5%.
Spam traps. Email service providers can add special spam trap mailboxes. Then if you send mail to such mailboxes you are identified as spam sender and your domain and IP reputation will decrease. There are cases when long abandoned user mailboxes become such spam traps — and that is another reason not to use old and unverified subscriber databases.
Complaints. Most of the email providers use "Report spam" button. When pressed it not only moves a message to Spam/Junk folder but creates a reputation precedent for the sending domain regardless whether you configure FBL or not. General recommendations specify 0.10% to be complaints threshold, but we recommend it to be no more than 0.07%, as several campaigns might have a higher than average complaint rate. To decrease this value make your emails more recognizable for your recipients and do not use content that cam be considered inappropriate or irrelevant.
Abuse. Sometimes recipients can issue a formal complaint to your senders' hosting, domains or IP adresses owner. There are organizations supervising spam rules compliance, like SpamCop. It is hard to eliminate such complaints totally - and even a single one can cause negative impact like IP or domain loss. In such cases hosting providers require subscribers opt-in information, including subscription date, time, IP address and URL. Make sure you can provide this data.
Behavioral. Besides "Report Spam" button all recipient activity influences your ISP reputation: message opens, link clicks, time spent reading emails.. The more subscribers' engagement - the better your ISP reputation.
Soft bounces. A lot of 4XX errors can ruin your reputation as well. Make sure you set correct retry and lock rules for temporarily undelivered emails.
Content. Your content is always one of the most important things for reputation. If your messages contain links to malicious software downloads or prohibited content advertising - it can bring negative effects to your sending domains and IP addresses.