Communication Channels Workflow
General Structure��
When a mailing is launched, the mailing binary is executed. It:
- processes the template and business logic (blocklists, limits, subscriptions, filters, etc.);
- builds the message structure for delivery;
- sends the prepared messages to RabbitMQ queues;
- records errors in the mailing log.
Each message then goes to the corresponding processing service depending on the channel.
Email
Several types of senders are supported for the email channel: AKMTA (the Altcraft sender) and external senders. The workflow may vary depending on the sender used.
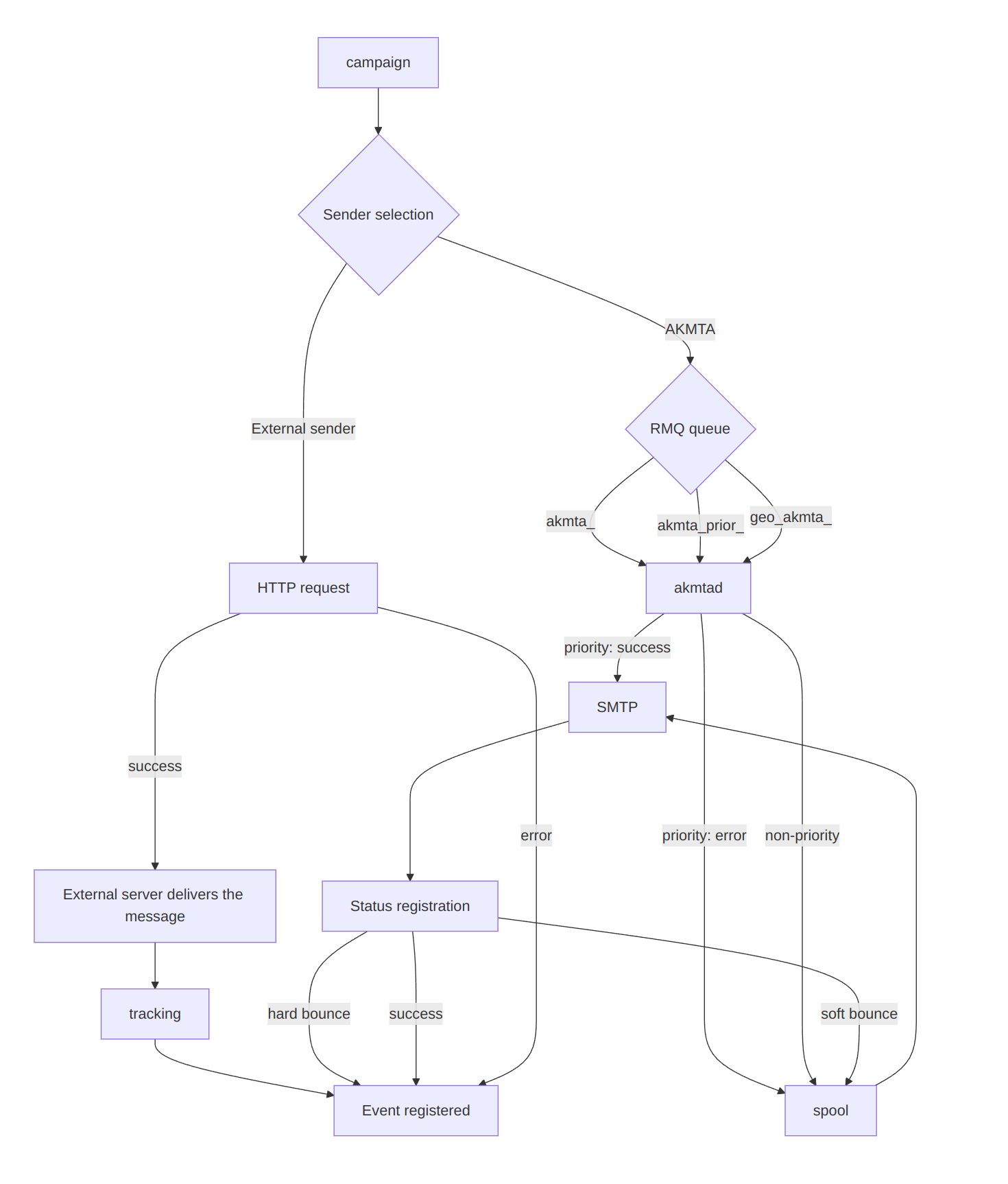
Sending Process
AKMTA
The mailing sends messages to the following queues:
akmta_<sender_id>— standard queue;akmta_prior_<sender_id>— priority queue.
Messages from the queues are processed by the akmtad service. Its behavior depends on the queue type:
- For a non-priority queue, it writes messages to disk, periodically reads them, and sends them according to the sending strategy configured for the specific
sender_id; - For a priority queue, it makes an attempt to send immediately; if it fails, it writes the message to disk.
The sending flow looks like this:
mailing → RMQ Queue (akmta / akmta_prior) → akmtad → SMTP
Other Senders
External senders receive messages via an HTTP request from the mailing binary. If the platform cannot send a message, a mailing error is logged. Note that such an error is not considered a "Non-Delivery" and is not included in the non-delivery report.
Status Registration
AKMTA
Delivery statuses are registered immediately using:
- the SMTP server response code;
- bounce patterns (analysis of bounce templates).
Other Senders
Tracking service of the platform handles event status.
Retry Logic
AKMTA
- Retry rules are defined separately in the Admin Panel. Details are available in the administrator documentation;
- Based on the SMTP code, hard bounce or soft bounce statuses are registered;
- Retry logic differs for soft and hard bounce cases.
Other Senders
External senders do not support retry attempts. If an HTTP request fails, the platform does nothing further.
SMS
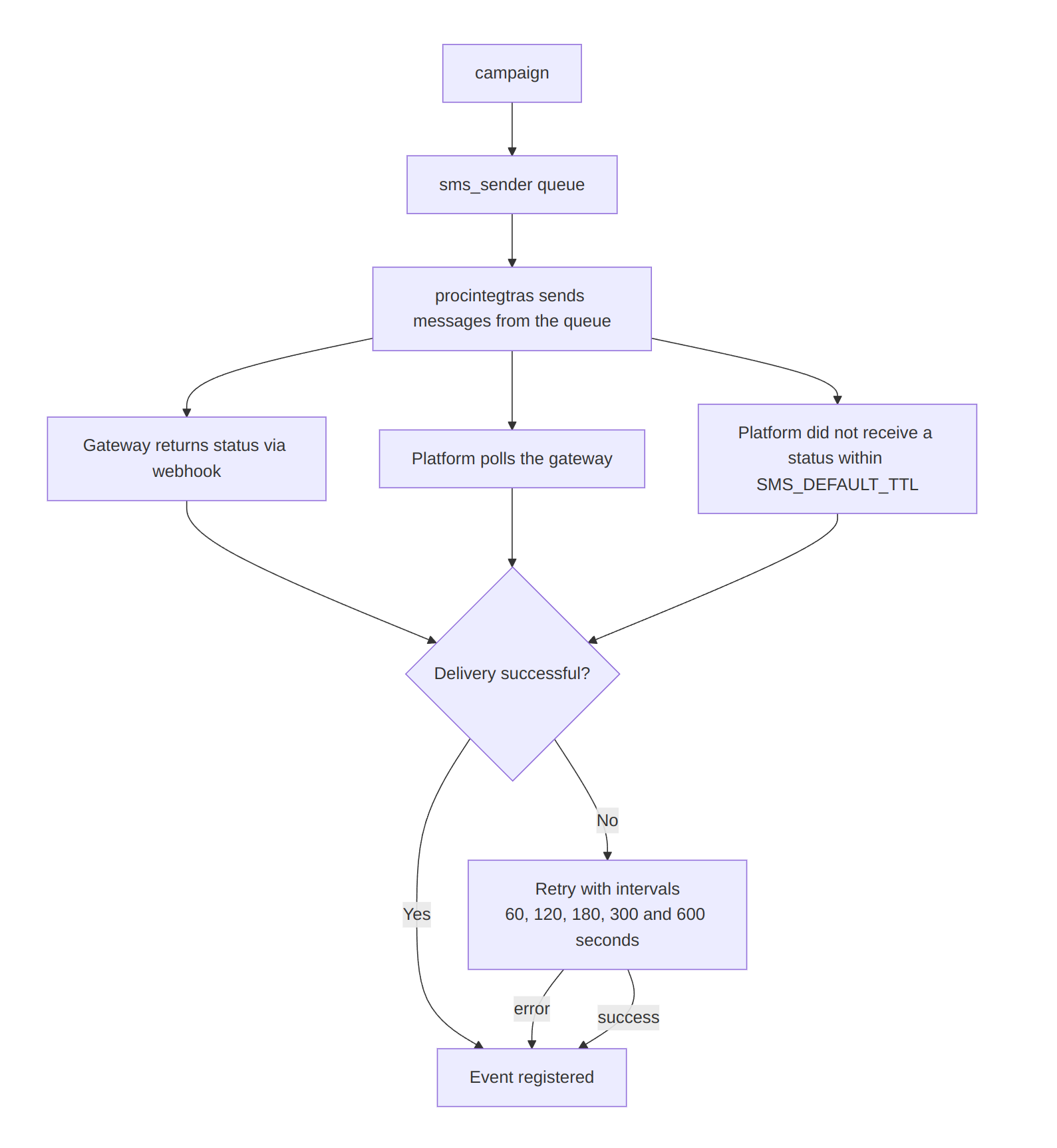
Sending Process
The mailing sends messages to a single queue — sms_sender. The procintegras service then sends messages from the queue. Some gateways support batch sending.
Status Registration
Status registration works in one of the following ways:
- The gateway sends a message status via a webhook. The status is processed by
procsmslisten; - The platform polls the gateway. The status is processed by
procsmsev.
The lifetime of an SMS message is defined by the configuration parameter SMS_DEFAULT_TTL (default — 1 day). The platform registers a non-delivery if no status is received within this time.
Retry Logic
SMS retries happen after 60, 120, 180, 300, and 600 seconds from the last failed attempt. The maximum number of attempts is 5.
Push
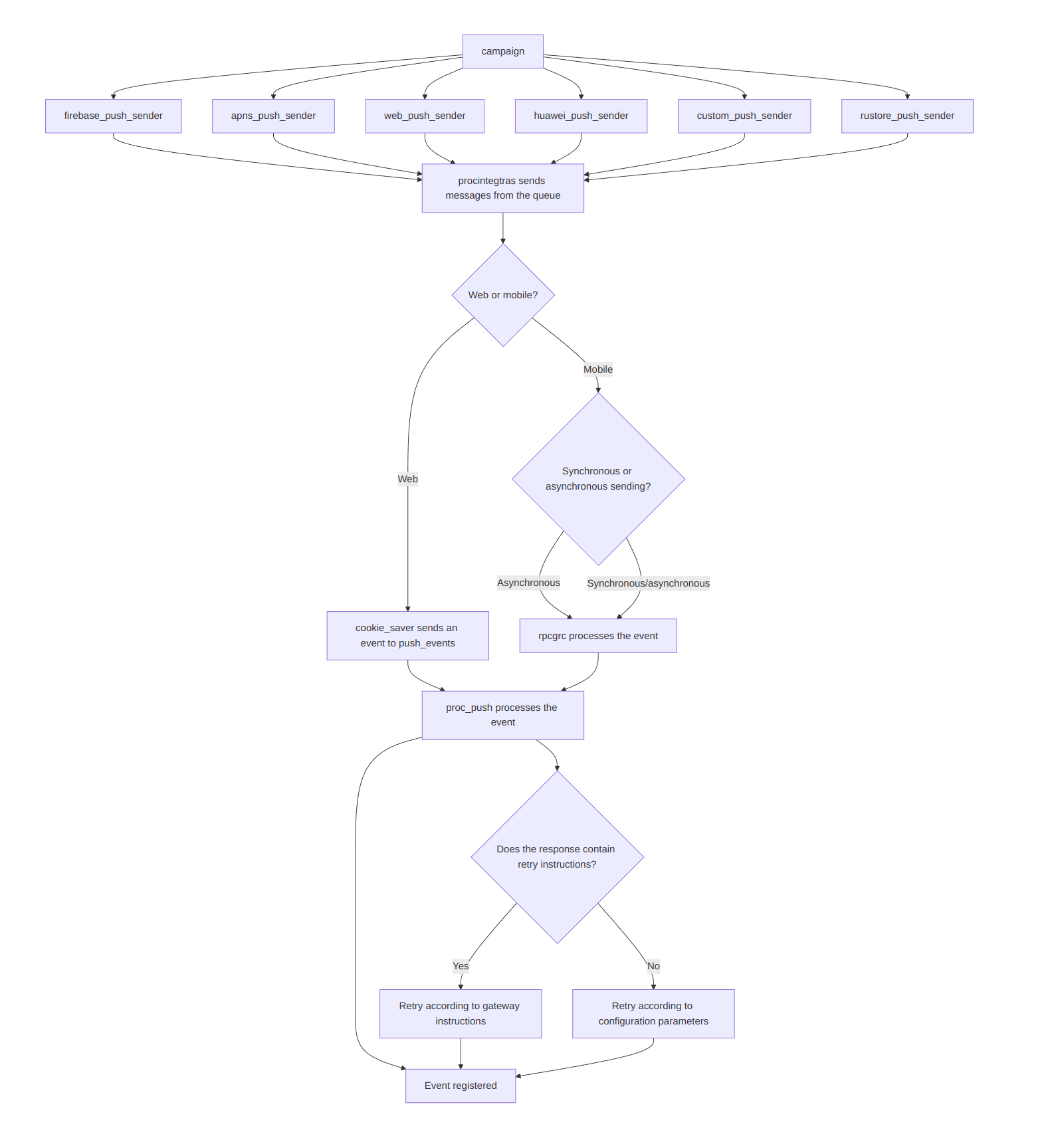
Sending Process
The mailing sends messages to a queue. The specific queue depends on the provider:
- APNs —
apns_push_sender - Firebase —
firebase_push_sender - Huawei —
huawei_push_sender - RuStore —
rustore_push_sender - Browser push (Firefox, Safari) —
web_push_sender - Other providers —
custom_push_sender
The procintegras service then sends messages from the queue. Some gateways support batch sending.
Status Registration
For browser push, the cookie_saver service handles status updates and sends events to push_events. Further processing occurs in procpush.
For mobile push, the logic is similar, but asynchronous sends are processed via push_events, while synchronous ones are immediately handled by procrpc.
The lifetime of a push message is defined by MTA_DEFAULT_TTL (default — 3 days). A non-delivery is registered if no status is received within this time.
Synchronous requests — the platform registers the result based on the response, meaning it waits for a reply.
Asynchronous requests — the platform registers the result when putting the message into the queue, meaning it does not wait for a reply.
Retry Logic
The sender checks the gateway’s response and headers to apply retry rules. If the gateway explicitly specifies retry instructions (for example, "try again in 5 minutes"), retries follow them. If not, the platform uses its configured parameters:
PUSH_SENDER_RETRY_MAX_AMOUNT— maximum retry count (default — 3);PUSH_SENDER_RETRY_INTERVAL— interval between retries (seconds) (default — 1800);PUSH_SENDER_RETRY_SCAN_INTERVAL— scan interval for retry records (seconds) (default — 60).
Detailed information is available in the administrator documentation.
Messenger Channels
Sending Process
The mailing sends messages to a queue. RabbitMQ queues are processed depending on the channel:
- Telegram Group, Telegram Bot — queue
piper_messages, processed byprocpiper; - Viber, WhatsApp, Notify — processed by
procintegras.
Status Registration
- Telegram — status is determined based on the HTTP response from Telegram. Delivery is registered if no error occurs during the send request. A non-delivery is registered if an error is returned.
- Viber, WhatsApp, Notify — statuses arrive via webhooks. If an error occurs during sending, a non-delivery event is registered. Statuses are handled by
trklisten.
Retry Logic
Messenger channels do not support retries at the moment.
Telegram imposes a limit of 28 requests per second per token.
For Notify, the default limit is 20 requests per second, configurable via VKNOTIFY_SEND_LIMIT_PER_SECOND, with a maximum of 50 requests per second.
For Viber, the default limit is 50 requests per second, configurable via VIBER_DEVINO_SEND_LIMIT_PER_SECOND.
For WhatsApp, the default limit is 20 requests per second (WHATSAPP_SEND_LIMIT_PER_SECOND); individual providers may apply their own request limits.