Nodes
Description
A Node is a network interface of the sending server used by AKMTA senders. A node can be located on the same server as Altcraft management components. However, the sending module is usually deployed on a separate server and connected to the management component via SSH or HTTPS protocols.
Different Altcraft deployment options are described in this article.
Instructions for adding IP addresses to a node are available here.
Creation, Editing, and Deletion
To manage nodes, in the main menu select Nodes.
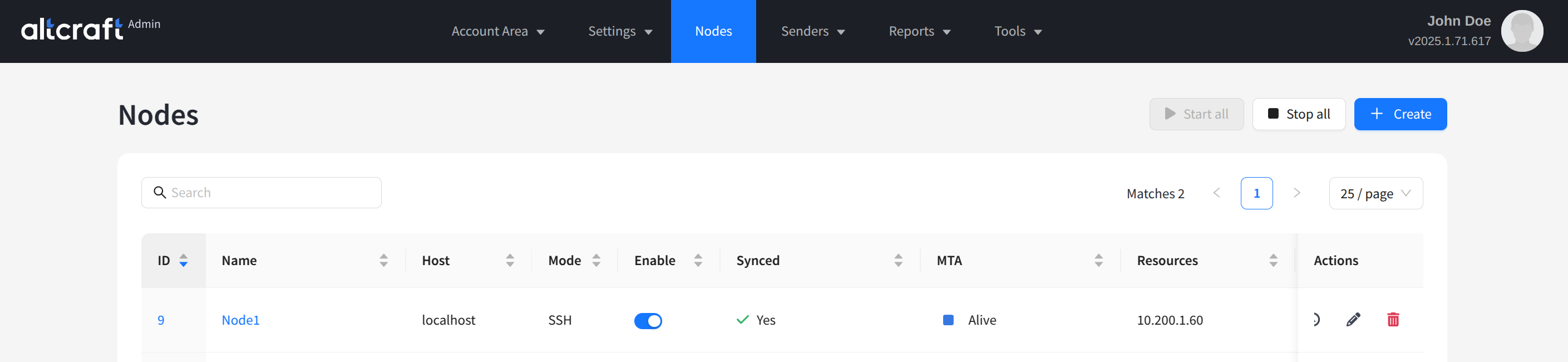
The list of existing nodes will appear. On the right side of the table, there are buttons for viewing error logs, editing, and deleting. You can also open editing by clicking on the name or ID of a node (on the left side).
In the node list, you can start or stop the MTA (mailer) on a specific node or on all available ones. After making changes, it is often necessary to restart the node so that the settings are synchronized with the Altcraft management server. The synchronization status is shown in the Synced column.
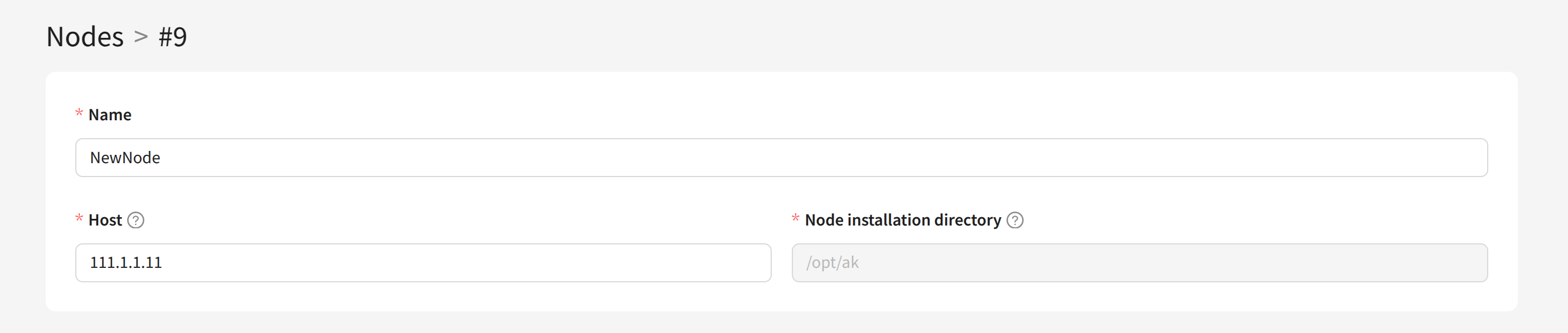
To create a new node, click + Create:
For the new node, specify a unique Name, the network Host address, and the Node installation directory on the sending server:
Node with SSH Access
By default, SSH protocol is used to access the server with the node. For this type of connection, you must specify the User and the SSH key:
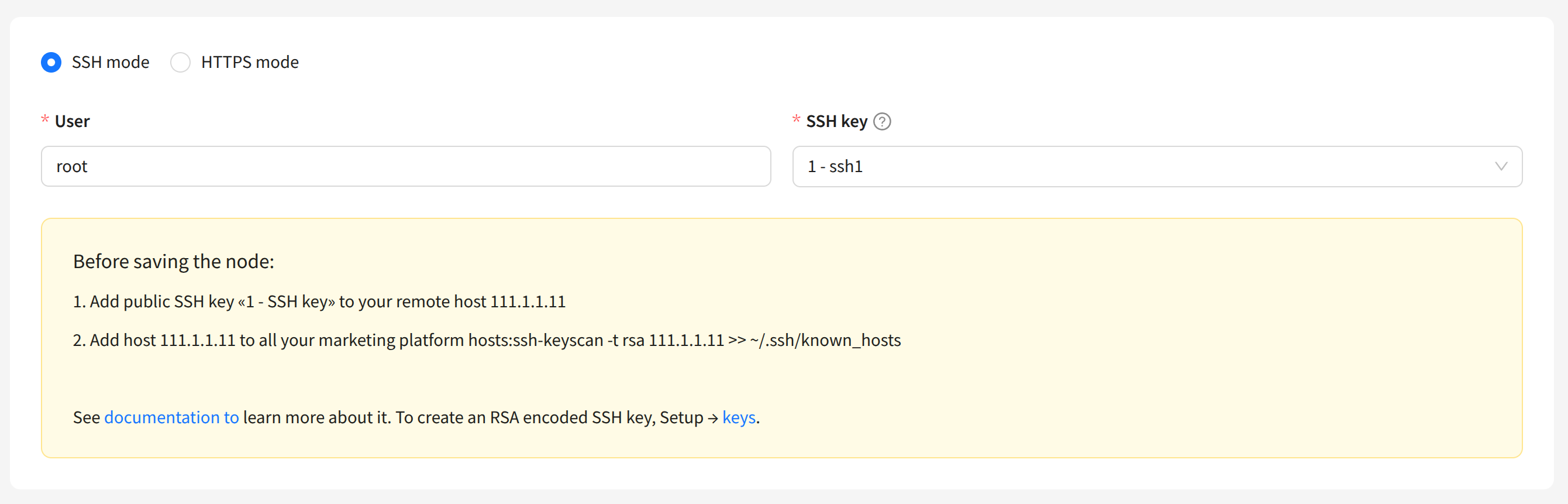
The SSH key must be created in advance in the platform. Learn more about how to do this here.
Node with HTTPS Access
A node using HTTPS connection must be manually installed on the sending server. The installation archive will be available for download after switching the node to HTTPS mode. You must also specify the API key for node access:
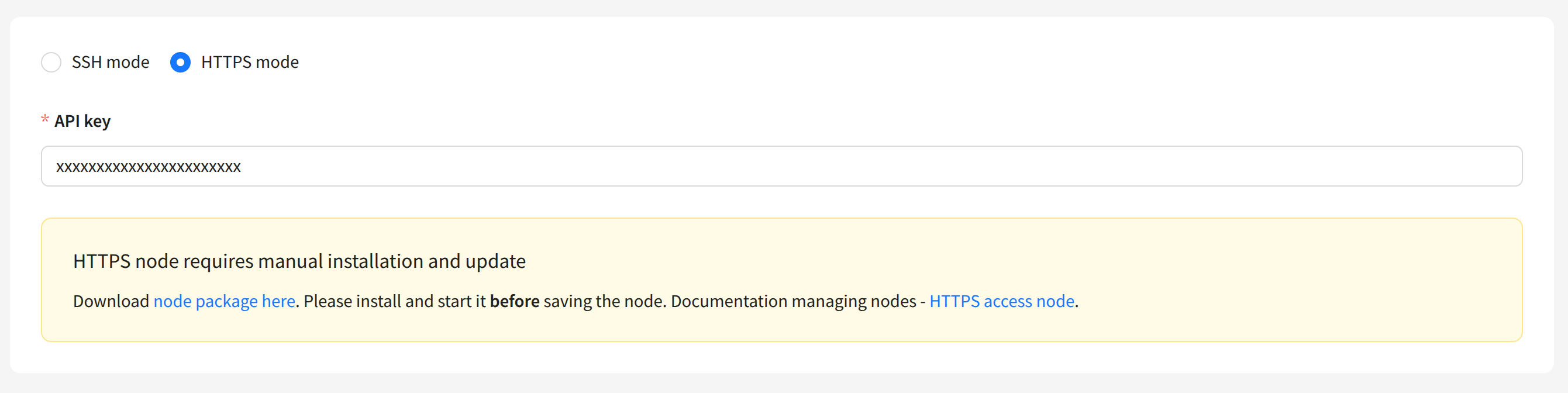
Unpack the node archive on the sending server and configure the node in the node.json file:
{
"LISTEN": "127.0.0.1:4433",
"CERT_PATH": "/opt/akmta_node/conf/server.crt",
"KEYFILE_PATH": "/opt/akmta_node/conf/server.key",
"APIKEY": "O46FtVEU1UdrMDwdCAORyDJelirt4r0W",
"PID_FILE": "/opt/akmta_node/node.pid",
"LOG_FILE": "/opt/akmta_node/node.log",
"BASEDIR": "/opt/akmta_node"
}
Example of starting the node:
./bin/node -d --https --config=/opt/akmta_node/conf/
Send Module Settings
For the send module using the node, you can configure data channel throughput, data retention time, and other parameters:
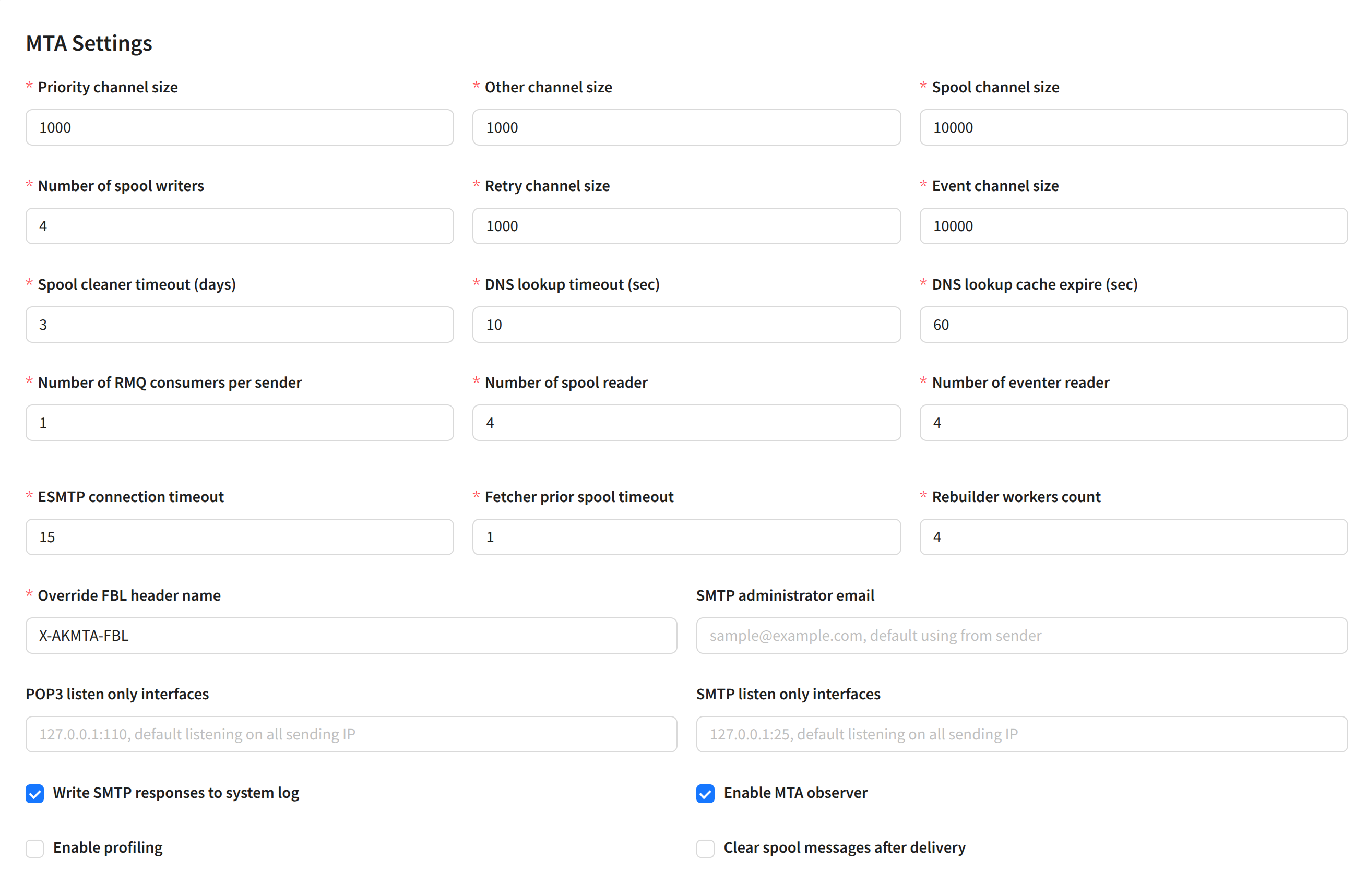
Data channel settings:
- Priority channel size — size of the high-priority sending channel (incoming).
- Other channel size — size of the main sending channel (incoming).
- Spool channel size — size of the outgoing sending channel (from the spool).
- Number of spool writers — number of concurrent threads writing to the spool from RabbitMQ.
- Retry channel size — size of the retry sending channel.
- Event channel size — size of the event processing channel.
- Spool cleaner timeout (days) — number of days before cleaning the spool (queue) on the node.
- DNS lookup timeout (sec) — DNS request timeout.
- DNS lookup cache expire (sec) — DNS cache expiration time in seconds.
- Number of RMQ consumers per sender — number of parallel RabbitMQ connections.
- Number of spool reader — number of spool readers.
- Number of eventer reader — number of event channel readers.
- ESMTP connection timeout — ESMTP connection establishment timeout.
- Fetcher prior spool timeout — buffer channel size for processing priority messages.
- Rebuilder workers count — number of internal service workers responsible for rebuilding expired messages.
- Override FBL header name — override the service header name for receiving complaint reports (FeedBack Loop).
- SMTP administrator email — administrator email address.
- POP3 listen only interfaces — select IPs for incoming mail responses (all selected by default).
- SMTP listen only interfaces — select IPs for outgoing mail responses (all selected by default).
- Write SMTP responses to syslog — log SMTP responses to syslog.
- Enable MTA observer — enable automatic MTA restart on the node by the management server in case of lost connection.
- Enable profiling — enable profiling (pprof).
- Clear spool messages after delivery — with this option enabled, delivered messages will be automatically deleted from the spool.
Debugging and Troubleshooting
Synchronizing Settings
After making changes to the sender configuration, you must synchronize the management and sending modules of Altcraft. When necessary, after saving the sender configuration, you will see this message:
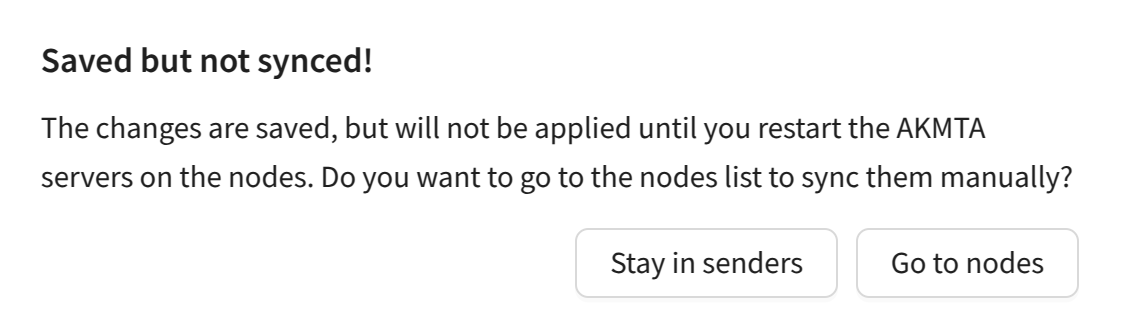
The list of nodes will open. You must stop and start the sender on the desired node by clicking Stop and Start in the MTA column: